- Order Online or Call
-
 (888) 474 - 9966
(888) 474 - 9966
-
-
Mon - Fri 9:00am - 3:00am EST - Se Habla Español
Sat - Sun 9:00am - 6:00pm EST
Glossary Of HVAC Terms
Here at The AC Outlet, we like our customers to be informed. Below are a list of common terms used in the HVAC Industry. We hope this list will help further educate you in the decision making process for your cooling and heating needs.
-
Advanced Reciprocating Compressor
Type of compressor that uses a more efficient process for compressing refrigerant for better cooling efficiency.
-
AFUE
Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency is indicated as a percentage. Your furnace's AFUE tells you how much energy is being converted to heat. For example, an AFUE of 90 means that 90% of the fuel is being used to warm your home, while the other 10% escapes as exhaust with the combustion gases.
-
Air Handler
The portion of your air conditioner or heating system that forces air through your home's ductwork.
-
Blower
In HVAC, the device in an air conditioner that distributes the filtered air from the return duct over the evaporator coil or heat exchanger. This circulated air is cooled or heated and then sent through the supply duct, past dampers and through supply diffusers to the living or working space.
-
Boiler
A vessel or tank where heat produced from the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, fuel oil or coal is used to generate hot water or steam for applications ranging from building space heating to electric power production or industrial process heat.
-
BTU
British Thermal Unit. Used for both heating and cooling, BTU is a measure of the heat given off when fuel is combusted. Or for cooling, it's a measure of heat extracted from your home.
-
BTU/H
A British Thermal Unit (BTU) is the unit of heat required to raise 1 pound of water by 1 degree Fahrenheit. BTU/H is British Thermal Units per Hour.
-
Building Envelope
Elements of the building, including all external building materials, windows and walls that enclose the internal space.
-
Capacity
The ability of a heating or cooling system to heat or cool a given amount of space. For heating, this is usually expressed in BTU's. For cooling, it is usually given in Tons.
-
Carbon Monoxide
A colorless, odorless, highly poisonous gas produced when carbon-based fuels, such as natural gas, burns without sufficient air nearby. Carbon monoxide is produced in the incomplete combustion of carbon and carbon compounds such as fossil fuels (i.e. coal, petroleum) and their products (e.g. liquefied petroleum gas, gasoline) and biomass.
-
Ceiling Plenum
Space below the flooring and above the suspended ceiling that accommodates thmechanical and electrical equipment and that is used as part of the air distribution system. The space is kept under negative pressure
-
Central Air Handling Unit
The same as an Air Handling Unit, but serves more than one area.
-
CFM
Stands for Cubic Feet per Minute. A measurement of airflow that indicates how many cubic feet of air pass by a stationary point in one minute. The higher the number, the more air is being forced through the system. 1 CFM equals approximately 2 liters per second (l/s).
-
Compressor
Part of a split-system heat pump or air conditioner's outdoor unit that controls the pressure applied to the refrigerant, necessary for taking in heat to warm your home with a heat pump or getting rid of heat to keep your home cool.
-
Condenser
The device in an air conditioner or heat pump in which the refrigerant condenses from a gas to a liquid when it is depressurized or cooled.
-
Condenser Coil
Part of the outdoor portion of a split-system air conditioner or heat pump. By converting refrigerant that is in a gas form back to a liquid, the coil sends heat carried by the refrigerant to the outside. This will return the hot vapor that entered the coil into a hot liquid upon exiting the coil.
-
Conditioned Air
Air that has been heated, cooled, humidified, or dehumidified to maintain an interior space within the "comfort zone."
-
Damper
A type of "valve" used in duct work that opens or closes to control airflow. Used in zoning to control the amount of warm or cool air entering certain areas of your home.
-
DB
Decibels (dB) are a unit measuring the intensity of noise.
-
Downflow
A type of furnace that takes cool air from the top and blows warm air to the bottom-commonly used where furnaces must be located in a second-floor closet or utility area.
-
Ductwork
Hollow pipes used to transfer air from the Air Handler to the air vents throughout your home. Ductwork is one of the most important components of a home heating and cooling system.
-
EER
Energy Efficiency Ratings (EER) measure the efficiency with which a product uses energy to function. It is calcuated by dividing a product's BTU output by its wattage.
-
Electronic Air Cleaner (EAC)
An electronic device that filters out large particles and contaminants in indoor air. It then electronically pulls out tiny particles that have been magnetized, such as viruses and bacteria, drawing them to a collector plate.
-
Energy Saver Switch
An energy-saver switch causes the air conditioner's fan and compressor to cycle on and off together, reducing energy use.
-
Energy Star
Energy Star is a government-backed program helping businesses and individuals protect the environment through superior energy efficiency. Products with the Energy Star rating will be efficient and save cost on energy bills.
-
Evaporator Coil
Part of a split-system air conditioner or heat pump located indoors. The evaporator coil cools and dehumidifies the air by converting liquid refrigerant into a gas (or vice-versa). A blower moter, typically in a furnace, then moves air over the coil to either heat or cool your home.
-
Fan Coil
An indoor component of an air conditioner or heat pump system, used in place of a furnace and evaporator coil, to provide change the refrigerant from a gas to a liquid (or vice-versa) and blow air over the coil to cool or heat your home.
-
Heat Exchanger
The part of a furnace that transfers heat to nearby air.
-
Heat Pump
A product that works just like an air conditioner in cooling mode; however, in heating mode, the refrigerant flow is reversed and heat is extrated from the outside air too heat your home.
-
HSPF
The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor is a measure of the heating efficiency of a heat pump. The higher the HSPF number, the more efficiently the heat pump heats your home.
-
Humidifier
A piece of equipment that adds water vapor to heated air as it moves out of the furnace. This adds necessary moisture to protect your furnishings and reduce static electricity.
-
HVAC
Term used for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning.
-
Hybrid Heat
Hybrid Heat systems deliver exceptional performance by using a heating source that provides the most energy-efficient comfort during moderate heating conditions.
-
IAP
Indoor air polution
-
IAQ
Indoor air quality
-
Indoor Coil
See Evaporator Coil
-
Infiltration
Air leakage inward through cracks and interstices and through cielings, floors, and walls of a space or building.
-
Ion
An electrically charged atom or group of atoms that has lost or gained electrons; a loss makes the resulting particle positively charged; a gain makes the particle negatively charged.
-
Load Estimate
A series of studies performed to determine the heating or cooling requirements of your home. An energy load analysis uses information such as the square footage of your home, window or door areas, insulation quality and local climate to determine the heating and cooling capacity needed by your furnace, heat pump or air conditioner. When referring to heating, this is often known as a Heat Loss Analysis, since a home's heating requirements are determined by the amount of heat lost through the roof, entry ways and walls.
-
Low Boy
Low Boy is a type of furnace configuration in which the furnace is lower in height and occupies more floor space.
-
Matched System
A heating and cooling system comprised of products that have been certified to perform at promised comfort and efficiency levels when used together, and used according to design and engineering specifications.
-
MERV
The Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value is the standard comparison of the efficiency of an air filter. The MERV scale ranges from 1 (least efficient) to 16 (most efficient), and measures a filter's ability remove particles from 3 to 10 microns in size.
-
Operating Cost
The day-to-day cost of running your home comfort equipment, based on energy use.
-
Outdoor Coil
See Condenser Coil.
-
Payback Analysis
Overall measure of the efficiency and value of your home comfort system. By combining your purchase price and ongoing operating costs, a payback analysis determines the number of years required before monthly energy savings offset the purchase price.
-
Puron Refrigerant
R-410A or Puron® Refrigerant is an environmentally sound refrigerant designed not to harm the earth's ozone layer. Federal law requires that all manufacturers phase out ozone depleting refrigerants in the next few years. Puron Refrigerant is approved by the US Environmental Protection Agency as a replacement from Freon 22.
-
QuieTech
QuieTech™ is a noise reduction system that provides comfortable heat while generating very little noise in the process.
-
R-22 Refrigerant
R-22 is a single component HCFC refrigerant with low ozone depletion potential. It has long been used in a variety of air-conditioning and refrigeration applications in a variety of markets. Production of R-22 will cease in 2015 per the Montreal Protocol.
-
Reciprocating Compressor
A type of compressor used in air conditioners that compresses refrigerant by using a type of "piston" action.
-
Reclaiming
Returning used refrigerant to the manufacturer for disposal or reuse.
-
Recycling
Removing, cleaning and reusing refrigerant.
-
Refrigerant Lines
Two copper lines that connect the Condenser (Outdoor) Coil to the Evaporator (Indoor) Coil.
-
Refrigeration Capacity
A measure of the effective cooling capacity of a refrigerator, expressed in Btu per hour or in tons, where one (1) ton of capacity is equal to the heat required to melt 2,000 pounds of ice in 24 hours or 12,000 Btu per hour.
-
Scroll Compressor
A specially designed compressor that works in a circular motion vs. an up and down piston action.
-
SEER
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio is a measure of the cooling efficiency of your air conditioner or heat pump. The higher the SEER number, the more efficient the system is at converting electricity into cooling power.
-
SEER2
Short for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2, SEER2 measures the efficiency of your air conditioning system over an entire cooling season. It contains standards that have been updated from SEER to make heating and cooling equipment more energy efficient. The higher the SEER2 rating on your HVAC system, the more energy efficient it is.
-
Setback Thermostat
A state-of-the-art electronic thermostat with a built-in memory that can be programmed for different temperature settings at different times of the day.
-
Single Package Product
One outdoor unit that contains both a heating and a cooling system.
-
Space Heater
A movable or fixed heater used to heat individual rooms.
-
Specific Humidity
The weight of water vapor per unit weight of dry air.
-
Split System
Refers to an air conditioner or heat pump that has components in two locations. Usually, one part of the system is located inside (evaporator coil) and the other is located outside your home (condenser coil).
-
Static Pressure
Condition that exists when an equal amount of air is supplied to and exhausted from a space. At static pressure, equilibrium has been reached.
-
Tankless Water Heater
A water heater that heats water before it is directly distributed for end use as required; also known as an on-demand water heater.
-
Temperature Zones
In HVAC, individual rooms or zones in a building where temperature is controlled separately from other rooms or zones.
-
Thermostat
Unit that monitors and controls your HVAC system products.
-
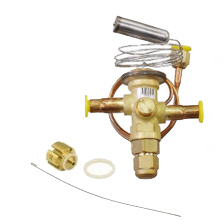
Thermostatic Expansion Valve
A thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) is precision device used to meter the flow of liquid refrigerant entering the evaporator at a rate that matches the amount of refrigerant being boiled off in the evaporator.
-
Ton
A unit of measure for cooling capacity. 1 Ton = 12,000 BTU's per hour.
-
Total Home Comfort System
The ultimate solution to providing you with consistent, customized home comfort, despite the ever-changing weather.
-
TrueSense Dirty Filter Detection
TrueSense™ dirty filter detection reminds you when it's time to change your media filter.
-
Two Stage Compressor
Two Stage Compressors are capable of two levels of operation, a low stage and a high stage. Properly sized equipment will operate 80% of the time in low stage, enhancing efficiency and comfort with lower humidity levels and quieter operation. It's like getting two air conditioners or heat pumps in one system.
-
UL
UL is an objective, non-profit organization that tests and rates electrical products for public safety.
-
Upflow
A type of furnace that draws cool air from the bottom and blows the warmed air out the top into the duct work. This type of furnace is usually installed in a basement or an out-of-the-way closet.
-
Ventilator
A ventilator captures heating or cooling energy from stale indoor air and transfers it to fresh incoming air.
-
Weatherization
In HVAC, caulking and weatherstripping to reduce air infiltration and exfiltration into/out of a building.
-
Weatherstripping
A material used to seal gaps around windows and exterior doors.
-
Zoning
A way to increase your home comfort and energy efficiency by controlling when and where heating and cooling occurs in a home. Programmable thermostats are used to control operating times of the equipment. Dampers are used to direct air flow to certain parts or "zones" of the home.